Super Micro Computer – weak start but strong outlook for 2026
After a slow start to the financial year, Super Micro Computer is forecasting a recovery in sales and a doubling of revenue in Q2, while the full-year target remains unchanged at 36 billion USD. The shares currently trade close to fair value.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. (NASDAQ: SMCI) reported Q1 results for the financial year 2026 with revenue of around 5.0 billion USD (–15% y/y) and non-GAAP earnings per share (EPS) of 0.35 USD, alongside a non-GAAP gross margin of 9.5%. These results were generally weaker than market expectations: both revenue and EPS came in below consensus and the company’s initial guidance range, though broadly in line with the recently revised forecast of about 5 billion USD. Management attributed the shortfall to the deferral of several large AI projects and server-rack deliveries to the next quarter due to configuration adjustments and delivery delays.
For Q2 FY 2026, the company expects revenue to rise to 10–11 billion USD and non-GAAP EPS of 0.46–0.54 USD, implying almost a doubling of sales compared with the reporting quarter. For the full 2026 fiscal year, Super Micro projects revenue of at least 36 billion USD, supported by a robust order backlog for AI servers and continued high levels of client investment in AI infrastructure.
This article examines Super Micro Computer, Inc., outlines the company’s key revenue streams, analyses its recent quarterly performance, and highlights its financial outlook for the financial year 2026. It also includes a technical analysis for SMCI shares, forming the basis for the Super Micro Computer, Inc. stock forecast for the 2026 calendar year.
About Super Micro Computer, Inc.
Super Micro Computer was founded in 1993 by Charles Liang. The company designs and manufactures server hardware, including motherboards, servers, data storage solutions, GPU systems, and other computing technologies. With proprietary manufacturing facilities in the Netherlands, the US, and Taiwan, it can tailor its products to the specific demands of different markets.
Super Micro employs a modular approach to deliver customised solutions for data centres, cloud services, and enterprise clients. The company went public on 29 March 2007, listing on the NASDAQ under the ticker SMCI.
Image of the company name Super Micro Computer, Inc.Super Micro Computer, Inc.’s primary revenue streams
Super Micro Computer generates revenue from the following sources:
- Server systems – the largest revenue segment, which includes:
##. Rackmount servers – high-performance servers designed for data centres, cloud computing, and AI workloads.
##. GPU-optimised systems – servers built for artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and deep learning applications.
##. Blade and multi-module servers – high-density solutions for enterprises and hyperscale environments.
- Data storage systems – this segment includes all-flash and hybrid storage solutions, as well as software-defined storage (SDS) architectures.
- Embedded and IoT systems – encompasses revenue from industrial and edge computing products, including IoT and edge servers used in smart cities, automation, and real-time data processing. It also includes industrial computing solutions for healthcare, telecommunications, and manufacturing.
- Networking and power technologies – this segment comprises:
##. High-performance networking equipment – Ethernet switches, network adapters, and interconnects for data centres.
##. Power supply units (PSUs) and cooling systems – modular, energy-efficient, and redundant power supplies, along with air and liquid cooling solutions.
- Components and accessories – revenue from individual hardware components, such as motherboards, chassis, processors, memory, storage devices, and accelerators.
Super Micro’s business model is centred on modular and customisable computing systems catering to enterprises, cloud providers, and the artificial intelligence industry.
Threat of delisting for Super Micro Computer, Inc. on NASDAQ
Super Micro Computer faced serious issues related to accounting practices and corporate governance, which led to the threat of its delisting from the NASDAQ exchange. Between 2014 and 2017, the company committed violations in revenue and expense reporting, prompting an investigation by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). In 2020, the SEC determined that the company and its former Chief Financial Officer had engaged in accounting violations, resulting in a settlement where Super Micro agreed to pay a fine of 17.50 million USD.
In 2018, Super Micro was temporarily removed from the NASDAQ listing due to delays in submitting its financial reports. The company failed to publish up-to-date financial data for nearly two years, causing concern among investors and regulators.
In 2024, the company again found itself at the centre of a scandal following the publication of an investigation by Hindenburg Research. The report alleged that Super Micro was engaged in questionable accounting practices and had ties to suppliers controlled by relatives of its CEO. These allegations sparked a new wave of doubts over the transparency of the company’s financial reporting.
An additional blow came when Super Micro decided to delay filing its annual report for the 2024 financial year, leading to a warning from NASDAQ about the possibility of delisting. The situation worsened in October 2024 when the auditing firm Ernst & Young declined to continue working with Super Micro, citing issues with internal controls, corporate governance, and potential violations of accounting practices. The auditor’s departure further exacerbated investor suspicions, contributing to a decline in the company’s stock price.
In response to the crisis, Super Micro’s Board of Directors established a special independent committee to investigate the allegations made by Ernst & Young and Hindenburg Research. In December 2024, the committee concluded its investigation, stating that there was no evidence of fraud or misconduct by the company’s management. Following this, NASDAQ granted Super Micro an extension until February 2025 to address its violations and submit all required reports.
Super Micro successfully avoided delisting by submitting a compliance restoration plan and appointing BDO USA as its new auditor. NASDAQ granted the company an extension until 25 February 2025 to submit the 10-K and 10-Q reports for the quarters ending 30 September and 31 December 2024. The company submitted all the required documents by the 25 February deadline, restoring its compliance with NASDAQ’s requirements and maintaining its listing. As a result, the delisting did not occur, but the episode highlighted serious issues with the company’s internal processes and eroded investor confidence.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. Q2 2025 financial results
On 25 February, amid the threat of delisting, Super Micro Computer released its Q2 2025 financial results for the quarter ended 31 December 2024. Below are the key figures:
- Revenue: 5.68 billion USD (+54%)
- Net profit: 320.59 million USD (+8%)
- Earnings per share: 0.51 USD (no change)
- Gross profit: 670.02 million USD (+18%)
Charles Liang, Chair and CEO of Super Micro, described Q2 FY2025 as relatively strong despite challenges, highlighting a 54% year-on-year revenue increase. This growth was driven by robust demand for AI solutions from both existing and new customers. He acknowledged certain obstacles, including cash flow pressures and market concerns regarding the delayed financial report. Liang identified the transition from Nvidia Hopper to Blackwell GPUs as a key growth factor, with supply expected to increase in the current quarter (Q3 FY 2025).
CFO David Weigand provided further details, noting that gross margin stood at approximately 11.9%, down from 13.1% in Q1 of the 2025 financial year, due to changes in product mix and customer base. He emphasised that AI-related platforms accounted for over 70% of revenue, reinforcing the company’s strong position in the enterprise and cloud provider markets.
For Q3 of the 2025 financial year, ended 31 March 2025, the company projected revenue in the range of 5.00–6.00 billion USD, signalling continued growth, although at a more moderate pace due to competitive dynamics in the AI server market.
Charles Liang has set an ambitious target of 40.00 billion USD in revenue by early FY2026, citing underutilised production capacity in Malaysia, the US, and Taiwan. He underscored Super Micro’s leadership in direct liquid cooling (DLC) technology, forecasting that over 30% of new data centres globally will adopt this technology within 12 months, positioning SMCI as a key player in this transition. Liang also highlighted plans to expand manufacturing operations in Europe, the US, and Taiwan to meet growing demand, particularly for AI infrastructure solutions.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. Q3 2025 financial results
On 6 May, Super Micro Computer released its Q3 2025 financial results for the quarter ended 31 March 2025. Below are the key figures:
- Revenue: 4.60 billion USD (+19%)
- Net profit: 108.77 million USD (–73%)
- Earnings per share: 0.31 USD (–53%)
- Gross profit: 440.21 million USD (–27%)
- Gross margin: 9.6% (–590 bps)
Super Micro recorded revenue of 4.6 billion USD, slightly above the revised forecast but still below Wall Street expectations, which had been buoyed by the AI euphoria earlier this year. Adjusted earnings per share stood at 0.31 USD, also lower than in previous quarters, suggesting that the hypergrowth phase had begun to slow, at least temporarily. Management attributed the shortfall to delays in customer orders and uncertainties in the supply chain.
A major strength remains the long-term driver of widespread adoption of AI infrastructure. Super Micro is at the centre of this trend, producing high-density server systems with liquid cooling that hyperscale clients actively purchase. A recent partnership with DataVolt demonstrates that the company is expanding its presence in the Middle East, where a data centre boom is underway.
Financially, the company appears stable, holding approximately 1.4 billion USD in cash on its balance sheet, although debt remains significant – around 1.9 billion USD – and is increasing. Moreover, much of the revenue growth in recent quarters has come from a very narrow segment: AI servers. Should this market cool (for example, due to saturation or increased competition from Dell, HPE, and NVIDIA), it would put pressure on margins.
The company’s guidance for Q4 2025 anticipates revenue of 5.6–6.4 billion USD and earnings per share in the range of 0.40–0.50 USD. However, the full-year revenue forecast has been lowered to 21.8–22.6 billion USD from the previous estimate of 23.5–25.0 billion USD, citing delayed customer spending and economic uncertainty.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. Q4 2025 financial results
On 5 May, Super Micro Computer, Inc. released its Q4 2025 financial results for the period ended 30 June 2025. Key financial results are as follows:
- Revenue: 5.76 billion USD (+7%)
- Net profit: 195.15 million USD (–34%)
- Earnings per share: 0.41 USD (–24%)
- Gross profit: 544.10 million USD (0%)
- Gross margin: 9.5% (–590 bps)
Super Micro Computer, Inc.’s Q4 2025 results came in below expectations. Revenue reached 5.8 billion USD versus forecasts of around 5.96 billion USD, primarily reflecting changes in contract terms with major clients and delays in the delivery of key components, including Nvidia GPUs. Non-GAAP earnings per share were 0.41 USD, also below market expectations. Non-GAAP gross margin declined to 9.5%, continuing its downward trend amid rising costs, including personnel, taxes, and logistics.
On a positive note, operating cash flow reached 864 million USD, reflecting strong conversion of revenue into cash and indicating resilient operational efficiency. Despite short-term challenges, the company delivered robust international growth: revenue in the Asia-Pacific region increased by 91% YoY, in EMEA by 66%, while the US market recorded a 33% decline.
Management reaffirmed its strategic focus on expanding the hyperscale and AI client base, targeting 6–8 major customers in FY 2026. Guidance for Q1 FY 2026 projects revenue in the range of 6–7 billion USD and non-GAAP EPS of 0.40–0.52 USD. For the full FY2026, the company expects revenue of at least 33 billion USD. However, some analysts consider this forecast overly optimistic, citing intensifying competition, declining margins, and reliance on a limited number of key clients.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. Q1 2026 financial results
On 5 May, Super Micro Computer released its Q1 results for the 2026 financial year (Q4 of the 2025 calendar year), ended on 30 June 2025. The key figures are as follows:
- Revenue: 5.02 billion USD (–15%)
- Net income: 239.90 million USD (–50%)
- Earnings per share: 0.35 USD (–52%)
- Gross profit: 474.45 million USD (–39%)
- Gross margin: 9.5% (–360 bps)
Super Micro delivered a weak quarter, missing market expectations: revenue of around 5.0 billion USD and non-GAAP EPS of 0.35 USD came in below analysts’ forecasts of approximately 5.8–6.0 billion USD in revenue and around 0.46 USD in EPS.
On a non-GAAP basis, profitability declined sharply year-on-year: gross margin fell to 9.5% from 13.1% a year earlier, adjusted net income decreased to about 240 million USD, and non-GAAP EPS dropped to 0.35 USD from 0.73 USD. Revenue contracted by roughly 15% year-on-year and around 13% quarter-on-quarter, while operating cash flow was negative at approximately –918 million USD due to higher inventory and receivables. The balance sheet shows 4.2 billion USD in cash and cash equivalents and about 4.8 billion USD in debt, indicating that the company moved into a modest net-debt position.
The main reason for the weak quarterly figures was the deferral of deliveries for several large AI projects at clients’ request, as they awaited new systems based on NVIDIA Blackwell and updated configurations. As a result, part of the existing order backlog was not recognised in the reported revenue.
Despite this, management issued an aggressive outlook: for Q2 FY 2026, the company expects revenue of 10–11 billion USD and non-GAAP EPS of 0.46–0.54 USD, implying nearly a twofold increase in quarterly sales. For the full financial year 2026, Super Micro targets revenue of at least 36 billion USD (up from a previous estimate of about 33 billion USD), supported by a rapidly growing order book, including over 13 billion USD in systems based on NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra. Management also reaffirmed its goal of sequential growth in each quarter of the year.
Fundamental analysis for Super Micro Computer, Inc.
Below is a fundamental analysis for SMCI based on the Q4 results of the 2025 financial year:
- Liquidity and access to funding: as of 30 September 2025, Super Micro held 4.2 billion USD in cash and equivalents, with current assets of 12.7 billion USD and liabilities of 2.35 billion USD – giving a high current ratio of around 5.4× and a quick ratio of about 2.9×. However, the asset structure has become riskier: inventories rose to 5.73 billion USD (+1.05 billion USD quarter-on-quarter), while receivables increased by 0.32 billion USD. In other words, part of the company’s capital is now tied up in working assets rather than cash.
Super Micro uses a mix of its own funds and borrowed capital: short-term credit lines totalled 100.6 million USD, long-term loans 25.2 million USD, and convertible bonds 4.65 billion USD. Overall, liquidity remains adequate, but cash declined by nearly 1 billion USD over the quarter owing to negative operating cash flow, which reduced the financial cushion compared with previous periods.
- Debt and leverage: total interest-bearing debt stood at 4.78 billion USD against 4.2 billion USD in cash, resulting in net debt of about 0.58 billion USD – the company is no longer in a net cash position but remains far from being highly leveraged. The debt-to-equity ratio is around 0.7×, which is still considered moderate.
Interest coverage remains comfortable: quarterly interest expenses were about 24.9 million USD, while adjusted EBITDA reached 335 million USD – implying over 13× interest coverage for the quarter. The key risk related to debt is not current interest payments but the large volume of convertible bonds, which will eventually need to be refinanced or converted into equity.
- Cash flow: operating cash flow (OCF) for the quarter was negative at around –918 million USD, compared with +409 million USD a year earlier. Including modest capital expenditure (~32 million USD), free cash flow was also around –950 million USD. Importantly, non-GAAP profit remained positive, indicating that the negative OCF was driven by a sharp increase in working capital rather than operational losses.
The main cash drains were a 1.09 billion USD rise in inventories, and a 321 million USD increase in receivables, along with a decline in payables and other short-term liabilities, partly offset by a 297 million USD increase in deferred revenue. This pattern is typical of a company building up inventory for major customers and shifting deliveries to the next quarter. However, such a large cash outflow (nearly 1 billion USD in three months) signals that if shipment delays persist or any orders are cancelled, liquidity could come under pressure. Nevertheless, by quarter-end, cash levels remained sufficient to cover this gap, and interest payments accounted for only a small portion of total cash flow.
Fundamental analysis for SMCI – conclusion:
From a financial stability perspective, Super Micro remains a profitable company with a solid balance sheet. However, the quality of that stability has weakened compared with prior periods. Management views this as a temporary effect ahead of large-scale shipments of systems based on NVIDIA Blackwell and other AI solutions. For Q2 of the 2026 financial year, the company forecasts revenue of 10–11 billion USD and at least 36 billion USD for the full fiscal year, implying strong growth in the coming quarters and a potential recovery in cash flow.
At this stage, SMCI’s fundamental picture can be summarised as follows: core solvency and debt-servicing capacity remain strong, and the risk of immediate financial distress is low, but the company’s resilience has become increasingly dependent on the successful execution of an ambitious AI-infrastructure growth plan. The key vulnerabilities are the large inventory build-up, exposure to the AI investment cycle, and lingering concerns about internal controls.
Analysis of key valuation multiples for Super Micro Computer, Inc.
Below are the key valuation multiples for Super Micro Computer, Inc. for Q1 of the 2026 financial year, calculated using non-GAAP metrics at a share price of 36 USD:
| Multiple | What it indicates | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| P/E (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of earnings over the past 12 months | 17.5 | ⬤ Moderate level – below the typical premiums seen in prominent AI stocks |
| P/S (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of annual revenue | 1.1 | ⬤ Very conservative revenue-based valuation for a fast-growing company |
| EV/Sales (TTM) | Enterprise value to sales, accounting for debt | 1.1 | ⬤ Close to normal for a hardware-focused business, showing no signs of overheating |
| P/FCF (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of free cash flow | 15.6 | ⬤ Not exceptionally cheap, but reasonable for a company in growth mode |
| FCF Yield (TTM) | Free cash flow yield to shareholders | 6.4% | ⬤ The stock offers a solid yield on free cash flow |
| EV/EBITDA (TTM) | Enterprise value to operating profit before depreciation and amortisation | 14.8 | ⬤ Slightly above the classic normal range (10–12×) but not excessive |
| EV/EBIT (TTM) | Enterprise value to operating profit | 15.3 | ⬤ Moderately expensive, yet still reasonable for a company with solid growth |
| P/B | Price to book value | 3.7 | ⬤ Market valuation stands noticeably above book value, though far from the extremes typical of pure AI stocks |
| Net Debt/EBITDA | Debt burden relative to EBITDA | 0.35 | ⬤ Very low debt – leverage-related financial risk remains minimal |
| Interest Coverage (TTM) | Ability to cover interest expenses with operating profit | 27 | ⬤ Interest expenses have virtually no impact on profitability |
Valuation analysis of Super Micro Computer, Inc. – conclusion
At the current share price, Super Micro Computer appears to be fairly valued. The market is pricing the company moderately for a hardware-focused business: its market capitalisation slightly exceeds annual revenue, while the free cash flow yield remains above the risk-free level.
The main risks lie in margin pressure and negative free cash flow resulting from rising inventories and working capital. If this proves temporary, the current price could be attractive for long-term investors; if not, the margin of safety may erode quickly.
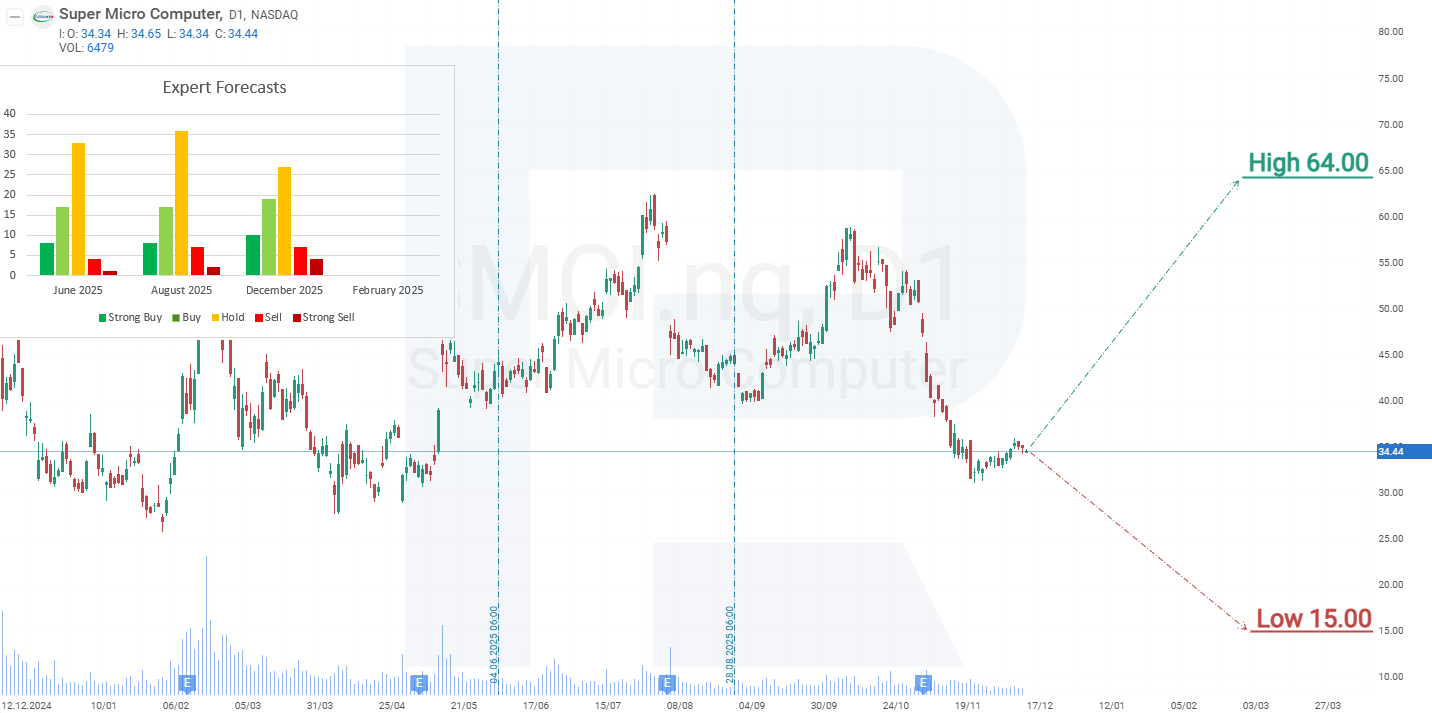
Expert forecasts for Super Micro Computer, Inc. stock
- Barchart: 5 out of 19 analysts rated Super Micro Computer shares as a Strong Buy, 3 as a Moderate Buy, 7 as Hold, 1 as Sell, and 3 as Strong Sell. The upper-end forecast is 64 USD, and the lower-end forecast is 15 USD.
- MarketBeat: 9 out of 19 analysts assigned the stock a Buy rating, 7 recommended Hold, and 3 advised Sell. The upper-end forecast is 64 USD, and the lower-end forecast is 34 USD.
- TipRanks: 5 out of 12 analysts rated the stock as Buy, 5 as Hold, and 2 as Sell. The upper-end forecast is 63 USD, and the lower-end forecast is 34 USD
- Stock Analysis: 5 out of 17 experts rated the stock as a Strong Buy, 2 as Buy, 8 as Hold, 1 as Sell, and 1 as Strong Sell. The upper-end forecast is 70 USD, and the lower-end forecast is 34 USD.
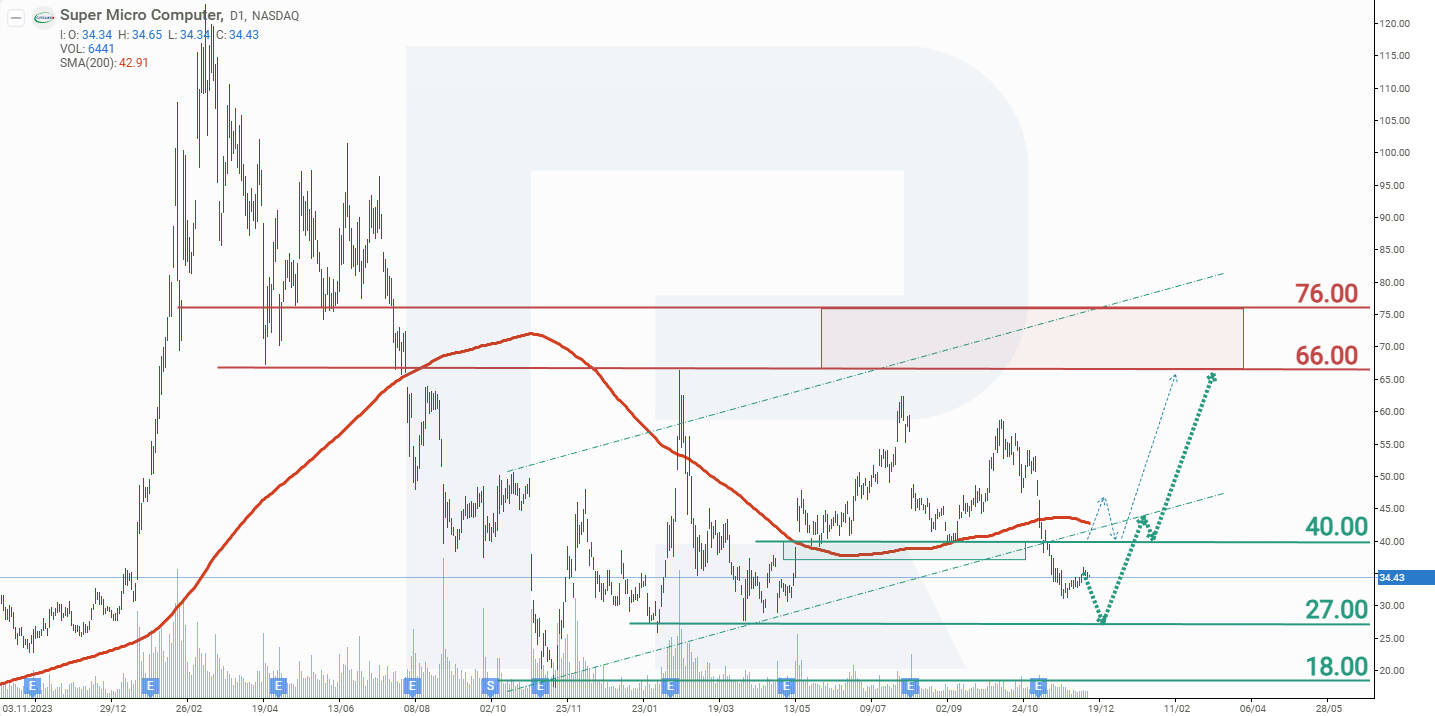
Super Micro Computer, Inc. stock price forecast for 2026
After an 85% decline from its all-time high, Super Micro Computer shares have yet to establish a sustained upward trend. The stock continues to trade within a broad range of 27 USD to 60 USD, occasionally moving beyond these boundaries. Following the release of the quarterly report, there have been no major changes – the share price has been gradually drifting towards the support level at 27 USD. Based on the current performance of Super Micro Computer’s share price, the potential scenarios for 2026 are as follows:
The base-case forecast for Super Micro Computer shares assumes a test of support at 27 USD, followed by a rebound towards 66 USD.
The alternative forecast for Super Micro Computer stock should be considered if the price breaks through resistance near 40 USD. In this scenario, the stock could advance towards 66 USD, and if that level is breached, it could continue climbing towards the next target at 76 USD.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. stock analysis and forecast for 2026Risks of investing in Super Micro Computer, Inc. stock
Investing in Super Micro Computer stock carries several factors that could negatively impact the company’s revenue and profits, ultimately affecting investor returns:
- Accounting issues: SMCI has a history of delays in financial reporting, including restatements and a fine of 17.50 million US dollars imposed by the SEC in 2020 for serious accounting violations.
- Dependence on major clients: a significant portion of SMCI’s revenue comes from a few key customers. Recent financial reports indicate that one of its largest clients accounted for approximately 22% of total revenue. Such high dependency poses risks, especially if these clients significantly reduce their order volumes.
- Increasing competition: the AI server market is becoming increasingly competitive. Companies like Dell Technologies (NYSE: DELL) and Wistron Corp. are actively developing similar solutions, which could lead to a decline in SMCI’s market share and put pressure on its profit margins.
- Stock sales by executives: recent large-scale stock sales by SMCI’s CEO and CFO have raised investor concerns about the company’s future prospects.
Forecasts presented in this section only reflect the author’s private opinion and should not be considered as guidance for trading. RoboForex bears no responsibility for trading results based on trading recommendations described in these analytical reviews.