Intel after Q4 2025 report: fundamental overview and INTC stock forecast for 2026
Intel reported Q4 2025 results exceeding expectations for both revenue and adjusted earnings. However, a weak Q1 2026 forecast triggered a sharp drop in shares.
For Q4 2025, Intel Corporation (NASDAQ: INTC) reported revenue of 13.7 billion USD, exceeding analysts’ consensus estimate of approximately 13.4 billion USD. Adjusted earnings came in at 0.15 USD per share, well above the expected 0.08 USD, while under GAAP, the company posted a loss of −0.12 USD per share. Year-on-year, revenue declined by 4%, but margins and operational efficiency were better than forecasted: the non-GAAP gross margin approached 38%, surpassing market expectations.
Growth was driven by the Data Center & AI segment, which posted a 9% year-on-year increase in revenue, while the consumer PC segment continued to decline. In the report, the company reaffirmed its focus on AI solutions and data centres as key drivers of future growth.
However, the Q1 2026 forecast disappointed the market: Intel expects revenue to be between 11.7 and 12.7 billion USD, with near-zero non-GAAP earnings, which is below analysts’ expectations. The weak forecast led to a sharp decline in shares after the report, even though the quarter’s actual performance exceeded expectations.
This article provides an overview of Intel Corporation, including a fundamental analysis of Intel’s reports and a technical analysis of INTC shares, based on which a stock forecast for Intel in 2026 is developed.
About Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation is a US technology company specialising in the development and production of microprocessors, chipsets, GPUs, systems-on-a-chip (SoC), network controllers, modems, flash memory, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth chipsets, and sensors for vehicle automation. Founded in 1968 by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce, Intel introduced the world’s first microprocessor in 1971, laying the groundwork for its future success.
In the same year, Intel held its initial public offering (IPO) on the NASDAQ under the ticker symbol INTC, becoming one of the first companies in the emerging technology sector.
Image of Intel Corporation nameChallenging times for Intel: the dot-com bubble, the pandemic, and competitive struggles
The company faced its first major setback during the dot-com bubble in 2000, when demand for PCs and servers plummeted. Management had increased production without anticipating the downturn, resulting in oversupply and falling prices. As a result, Intel was compelled to scale back production, cut costs, and develop a recovery program. Following the crisis, the technology market rebounded, reviving demand for Intel’s products and helping the company recover from the downturn.
The next major test came in 2021. A surge in demand for semiconductor products during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 drove increased production, leading to market oversaturation and a subsequent price drop, which, in turn, hit Intel’s revenue. However, the company’s challenges did not end there.
In 2023, Intel faced fierce competition from AMD and NVIDIA, whose products outperformed Intel’s processors and graphics solutions in both performance and energy efficiency. A key factor behind this loss of competitiveness was the previous management’s focus on business strategy and financial performance at the expense of engineering investment, leading to delays in transitioning to more advanced 7- and 5-nanometre technologies – already mastered by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (NYSE: TSM), which produces chips for NVIDIA and AMD.
Investors’ reaction to the company’s difficulties was obvious – they sold off Intel shares. During the 2000 dot-com crisis, the company’s stock plunged by 82%. The current situation is similar, with the stock losing 70% of its value between its April 2021 peak and November 2024.
Intel is increasing investments in new factories and equipment upgrades for foundry operations to restore investor confidence and defend its market share. This strategy temporarily reduces profitability (the company ended 2024 with a loss). Intel’s management plans to lay off up to 15% of its workforce to reduce costs.
Intel Corporation Q3 2024 results
Intel released its Q3 2024 report on 31 October, revealing the following key financial indicators:
- Revenue: 13.3 billion USD (–6%)
- Net income (loss): 2.0 billion USD compared to 1.7 billion in Q3 2023
- Earnings (loss) per share: 0.46 USD compared to 0.41 USD in Q3 2023
- Gross Margin: 18.0% (–2,780 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- Client Computing Group: 7.3 billion USD (–7%)
- Data Center and AI: 3.3 billion USD (+9%)
- Network and Edge: 1.5 billion USD (+4%)
- Intel Foundry: 4.4 billion USD (–8%)
- All other: 1.0 billion USD (–28%)
In her comments on the report, Intel’s CEO, Pat Gelsinger, noted that the company’s profitability was impacted by expenses previously mentioned during the Q2 2024 results discussion. However, the actual results exceeded expectations. In Q3, Intel took significant steps to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and strengthen its market competitiveness. A substantial part of the workforce reduction program was also implemented, with plans to lay off an additional 15% of employees by the end of 2024.
The financial results were also impacted by write-offs of outdated products from the COVID-19 period, as these could not be integrated into current products.
Management had an optimistic outlook for Q4 2024. Revenue was projected in the 13.3–14.3 billion USD range, with adjusted EPS at 0.12 USD, reinforcing the possibility of the company returning to profitability.
Despite the current losses, Intel is encouraging shareholders to retain their shares and has paid a Q3 dividend of 0.12 USD per share.
Intel Corporation Q4 2024 results
On 30 January, Intel released its Q4 2024 report with the following key figures:
- Revenue: 14.3 billion USD (–7%)
- Net income (loss): (126) million USD compared to income of 2.7 billion in Q4 2023
- Earnings (loss) per share: (0.03) USD compared to earnings of 0.63 USD in Q4 2023
- Gross margin: 32.9% (–650 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- Client Computing Group: 8.0 billion USD (–9%)
- Data Center and AI: 3.4 billion USD (–3%)
- Network and Edge: 1.6 billion USD (+10%)
- Intel Foundry: 4.5 billion USD (–13%)
- All other: 1.0 billion USD (–20%)
For Q1 2025, Intel projected revenue in the 11.7–12.7 billion USD range and a loss of 0.27 USD per share. The gross margin was expected at 36%, down from 51% in Q1 2024.
Q4 2024 marked the first financial quarter under the interim co-presidency of David Zinsner and Michelle Johnston Holthaus following the departure of Pat Gelsinger. Michelle Holthaus noted that the last quarter represented a positive step forward, as Intel exceeded its revenue, gross margin, and EPS forecasts. She emphasised the progress in executing the cost-cutting plan aimed at supporting the company’s recovery. David Zinsner stated that the plan had a positive impact, contributing to improved business efficiency, return on invested capital, and the company’s overall profitability.
Intel continues to move towards its foundry model by establishing Intel Foundry as a separate subsidiary. For Q1 2025, revenue from this division was expected to remain in line with Q4 2024 levels.
Despite positive elements in the company’s report, market participants reacted negatively to its release due to the anticipated decline in Intel’s revenues.
Intel Corporation Q1 2025 earnings results
On 25 April, Intel published its results for Q1 2025, which ended on 29 March. The key figures are presented below, compared with the same period in 2024:
- Revenue: 12.7 billion USD (0%)
- Net income (loss): 887 million USD compared to a loss of 437 million USD in Q1 2024
- Loss per share: 0.13 USD compared to a loss of 0.09 USD in Q1 2024
- Gross margin: 39.2% (–590 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- Client Computing Group: 7.6 billion USD (–8%)
- Data Centre and AI: 4.1 billion USD (+8%)
- Intel Foundry: 4.7 billion USD (+3%)
- All other: 0.9 billion USD (+47%)
Intel’s Q1 2025 report delivered mixed results. On the one hand, the company exceeded revenue expectations; on the other, it reported a net loss of 821 million USD – its fourth consecutive quarterly loss.
Management issued a cautious outlook for Q2 2025. Revenue was projected to range between 11.2 billion and 12.4 billion USD, with a potential loss per share of up to 0.32 USD. These figures fell short of Wall Street’s expectations. Chief Financial Officer David Zinsner attributed this cautious stance to ongoing macroeconomic uncertainty, including trade tensions and potential new tariffs, which had impacted customer behaviour at the start of the year.
Under new CEO Lip-Bu Tan, Intel has embarked on a large-scale restructuring. Key measures include reducing management layers to speed up decision-making, introducing a four-day office working week to boost productivity, and lowering operating expenses to 17 billion USD in 2025 and 16 billion USD in 2026.
Nevertheless, the company continued to face significant challenges in the AI segment, where its competitors Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA) and AMD (NASDAQ: AMD) firmly hold leading positions. Intel’s AI initiatives, including its Gaudi accelerators, have so far fallen short of expectations, while plans to launch the Falcon Shores GPU have been scaled back.
Intel Corporation Q2 2025 earnings results
On 24 July, Intel released its earnings report for Q2 2025, which ended on 28 June. Key figures, compared with the same period in 2024, are outlined below:
- Revenue: 12.86 billion USD (0%)
- Net loss: 400 million USD compared to a profit of 100 million USD in Q2 2024
- Loss per share: 0.10 USD compared to a profit of 0.02 USD in Q2 2024
- Gross margin: 29.7% (–900 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- Client Computing Group: 7.9 billion USD (–3%)
- Data Center and AI: 3.9 billion USD (+4%)
- Intel Foundry: 4.4 billion USD (+3%)
- All other: 1.1 billion USD (+20%)
In Q2 2025, Intel reported revenue of 12.9 billion USD, which was nearly flat year‑on‑year and slightly above analyst expectations. Despite this, the company posted a non‑GAAP adjusted loss of 400 million USD, or 0.10 USD per share. This result was due to high one‑off costs, including 1.9 billion USD in restructuring expenses, 800 million USD in asset write‑downs, and an additional 200 million USD in charges.
For Q3 2025, Intel expected revenue to range between 12.6 and 13.6 billion USD, broadly in line with current levels. The non‑GAAP gross margin was forecast at 36%, with earnings per share anticipated to be around breakeven. Under GAAP, the company projected a loss of 0.24 USD per share, with a gross margin of 34.1% and a negative tax rate. This forecast reflected continued pressure on profitability, while also signalling efforts to stabilise financial performance through cost control and a focus on core products.
Intel’s Q2 2025 results highlighted several ongoing challenges. First, the company faced significant pressure on profitability due to restructuring and major write‑downs, which reduced both gross and operating margins.
Second, Intel continued to struggle to attract external clients to Intel Foundry Services (IFS), which provides contract chip manufacturing. The Foundry segment generated around 4.3 billion USD in Q2 revenue, but this was almost entirely from internal orders. Revenue from third‑party clients was minimal at just 22 million USD – a negligible figure given the substantial investments made in this area. This indicates that IFS has yet to establish itself as a serious competitor to players like TSMC and Samsung in the foundry market. Intel continues to promote the Foundry direction as strategically important and placed its bets on Intel 18A process technology. Still, full commercial adoption by external customers remains at a very early stage.
Nonetheless, there are potential growth areas within the company. The Data Center and AI segment grew by 4%, IFS rose by 3%, and there was a notable +20% increase in Mobileye and other niche areas, reflecting early signs of positive momentum.
The new leadership under CEO Lip‑Bu Tan is restructuring the corporate organisation, reducing costs, reassessing capital investments, and focusing on key products – including the development of AI processors and the next generation of Intel 18A chips: Panther Lake and Clearwater Forest, which are expected to launch in 2025–2026.
Intel currently presents a moderately risky profile. From a long‑term perspective, for investors willing to tolerate earnings volatility in exchange for potential upside from AI and IFS, the current price range may offer an attractive entry point. However, for those seeking more stable short‑term returns, there are less volatile and more profitable alternatives in the sector, such as Texas Instruments (NASDAQ: TXN), Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (NYSE: TSM), and Broadcom Inc. (NASDAQ: AVGO).
Intel Corporation Q3 2025 results
On 23 October, Intel released its financial results for Q3 2025, which ended on 27 September. The key figures compared with the same period in 2024 are as follows:
- Revenue: 13.65 billion USD (+3%)
- Net income (non-GAAP): 1.02 billion USD, compared with a loss of 1.97 billion USD in Q3 2024
- Earnings per share (non-GAAP): 0.23 USD, compared with a loss of 0.46 USD in Q3 2024
- Gross margin: 40.0% (+22 percentage points)
Revenue by segment:
- Client Computing Group: 8.54 billion USD (+5%)
- Data Centre and AI: 4.12 billion USD (–1%)
- Intel Foundry: 4.24 billion USD (–2%)
- All other: 0.99 billion USD (+3%)
Intel delivered results ahead of expectations, with both revenue and non-GAAP EPS exceeding forecasts. The gross margin came in above the July guidance, and instead of the GAAP loss projected in the previous quarter, the company posted a net profit of 4.1 billion USD. In Q3 2025, most of the GAAP profit was driven by one-off factors – the partial sale of Intel’s stake in Mobileye and the spin-off of Altera into a separate entity. Excluding these effects, results would have been more modest, with adjusted EPS (non-GAAP) at 0.23 USD. Operating expenses declined, helping to support margins, while operating cash flow totalled about 2.5 billion USD.
The Foundry segment remained the company’s weak spot, with revenue of 4.2 billion USD and a loss of 2.3 billion USD, driven by high costs related to the rollout of the 18A process technology and low factory utilisation. Nevertheless, Intel highlighted progress: the fab has reached full capacity, and a new partnership with NVIDIA could help boost contract-manufacturing orders.
Intel’s management reported that demand currently exceeded supply and is likely to remain so until 2026. This should help keep prices stable, but increases the risk of supply-chain disruptions.
For Q4 2025, Intel expected revenue of 12.8–13.8 billion USD, gross margin of around 36.5%, and non-GAAP EPS of about 0.08 USD. The forecast did not include Altera’s results following its divestment. Overall, the quarter was stronger than expected; however, the year-end outlook indicated continued pressure on profits and margins, particularly within the Foundry segment.
Intel Corporation Q4 2025 results
On 22 January, Intel published its Q4 2025 results, covering the period ended 27 December. Below are the key figures compared to the same period in 2024:
- Revenue: 13.67 billion USD (–4%)
- Net income (non-GAAP): 0.77 billion USD (+35%)
- Earnings per share (non-GAAP): 0.15 USD (+15%)
- Gross Margin: 37.9% (–4.2 percentage points)
Revenue by Segment:
- Client Computing Group: 8.19 billion USD (–6%)
- Data Center and AI: 4.74 billion USD (+9%)
- Intel Foundry: 4.51 billion USD (+4%)
- All other: 0.57 billion USD (–48%)
Intel reported stronger-than-expected results for Q4 2025. Revenue totalled 13.7 billion USD, surpassing analysts’ forecast of approximately 13.4 billion USD, and adjusted earnings per share reached 0.15 USD, well above the expected 0.08 USD. Under GAAP, the company still posted a loss of 0.12 USD per share.
The business picture is mixed. The Data Center & AI segment grew by 9% year-on-year and was the primary source of the improved results. However, the PC market continues to weaken, and sales in the client segment are declining. Gross margin remains under pressure, indicating high production costs and Intel’s challenging competitive position.
The key negative came from the guidance. For Q1 2026, management expects revenue between 11.7 and 12.7 billion USD and virtually zero non-GAAP EPS. This forecast was notably worse than market expectations, pointing to a weak start to 2026. The company also acknowledged that issues with manufacturing, supply, and yield of functional chips would persist at least until the second quarter.
The weak guidance caused a sharp decline in shares after the report. Despite a strong quarter, investors are more concerned about future growth rates, and the low guidance for early 2026 heightened concerns that Intel’s business recovery will be slow. Additionally, in 2026, Intel decided to reallocate its manufacturing resources, prioritising Xeon server processors for data centres and AI infrastructure. This decision is driven by increased demand for data centre chips. While Intel has not abandoned the PC market, it is reducing its focus on budget and low-margin solutions and betting on more expensive processors. This approach may support profitability, but it creates a risk of further weakening positions in the mass-market PC segment, where competitors are likely to increase their market share.
Fundamental analysis for Intel Corporation
Below is the fundamental analysis for INTC for Q3 2025:
- Liquidity: Intel’s liquidity improved at the end of 2025 compared to the previous year. At the beginning of 2025, cash and cash equivalents amounted to 8.25 billion USD, and by the end of 2025, this figure increased to 14.27 billion USD. Current assets grew from 47.32 billion USD in 2024 to 63.69 billion USD in 2025. Liquidity ratios improved, providing the company with greater short-term operational flexibility. Total current liabilities decreased from 35.67 billion USD in 2024 to 31.58 billion USD in 2025. Accounts receivable stood at 3.84 billion USD, showing little change, which could potentially tie up working capital.
- Debt and financial stability: Intel continues to bear a significant debt burden. As of the end of 2025, the company’s long-term debt stood at 44.09 billion USD, down from 46.28 billion USD the previous year. As a result, the debt-to-equity ratio is around 40%, which is moderate for a large technology company; but the debt and interest coverage ratios are under pressure due to weak profitability. Credit rating agencies recently downgraded Intel’s credit rating to BBB with a negative outlook, reflecting concerns about the volatility of its earnings and the risks of meeting its obligations.
- Profitability and earnings: Intel’s profitability continues to recover, showing improvements in non-GAAP metrics, but it is facing challenges under GAAP accounting. The GAAP gross margin in 2025 dropped to 34.8% (down from 32.7% in 2024), and in Q4 2025, it stood at 36.1%, which is considerably lower than historical levels. Meanwhile, Intel’s net loss in Q4 2025 was 591 million USD, and the total net loss for 2025 was 267 million USD.
Regarding non-GAAP metrics, there was improvement, slightly exceeding market expectations. Non-GAAP EPS for Q4 2025 was 0.15 USD, and for the full year, it was 0.42 USD. The annual non-GAAP gross margin increased to 36.7% (from 36.0% in 2024), while the quarterly margin was 37.9%, indicating better cost control and operational efficiency despite ongoing challenges. However, the revenue decline in key segments indicates strong competitive pressure. Revenue in the client computing segment decreased by 7%. In the discrete GPU market, Intel’s share fell to nearly zero in Q1 2025, while NVIDIA captured around 92% of the market. In the server processor segment, Intel’s share decreased to 72% in 2025, while AMD’s share rose to nearly 30%.
- Cash Flow and Investments: operating cash flow for the quarter was positive, amounting to 4.29 billion USD, with capital expenditures (CapEx) totalling 4.02 billion USD, resulting in a small positive free cash flow after capital investments. This indicates that Intel continues to generate cash from its operations, but large investments in production and supply chain costs restrict surplus free cash flow.
Fundamental Analysis for Intel – conclusion
Intel’s Q4 2025 results show a company still in the process of transformation rather than stable growth. Liquidity and cash flows have improved, providing a buffer for operations, but significant debt and ongoing GAAP losses weaken the financial structure. Profitability metrics are mixed: operational cost control has improved, but net losses and margin compression persist. Positive operating cash flow and disciplined investments indicate the ability to generate cash, but high capital expenditures and competitive pressures are limiting liquidity surpluses. For investors, Intel’s financial stability in Q4 2025 is considered unstable.
Analysis of key multiples for Intel Corporation
Below are the key valuation multiples for Intel Corporation as of Q4 2025, calculated based on a share price of 42 USD.
| Multiple | What it indicates | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| P/E (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of earnings over the past 12 months | N/A | ⬤ Negative earnings – P/E is not applicable. This signals business instability. |
| P/S (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of annual revenue | 4.0 | ⬤ Moderately high valuation. For Intel, it is crucial to maintain revenue growth, especially in the Foundry and data centre segments. |
| EV/Sales (TTM) | Enterprise value to sales, accounting for debt | 4.4 | ⬤ Valuation above the average, indicating expectations of business growth. |
| P/FCF (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of free cash flow | N/A | ⬤ P/FCF loses relevance due to being close to zero. Intel spends almost all its operating cash flow on investments. |
| FCF Yield (TTM) | Free cash flow yield to shareholders | -0.1% | ⬤ A negative FCF yield indicates that the company is not generating free cash flow, making investing in it more speculative. |
| EV/EBITDA (TTM) | Enterprise value to operating profit before depreciation and amortisation | 16.1 | ⬤ Close to the upper limit of a reasonable range. Without EBITDA growth, this multiple will pressure the stock price. |
| EV/EBIT (TTM) | Enterprise value to operating profit | 88.4 | ⬤ Extremely high valuation. With the current EBIT, investors are pricing in an aggressive recovery. |
| P/B | Price to book value | 1.8 | ⬤ A normal level for a capital-intensive company. |
| Net Debt/EBITDA | Debt burden relative to EBITDA | 3.2 | ⬤ Moderate debt load. It is acceptable for now, but caution is required given the weak cash flow. |
| Interest Coverage (TTM) | Ability to cover interest expenses with operating profit | 2.43 | ⬤ The minimum acceptable level. The company can still service its debt, but the margin of safety is decreasing. |
Intel Corporation's valuation multiples analysis – conclusion
The company is in a transition phase, and the market has largely priced in expectations of future recovery driven by AI, Foundry, and data centre segments. However, the current picture remains weak: GAAP earnings are negative, free cash flow is limited, and the company’s valuation remains high even based on revenue and EBITDA metrics. That said, they may be expensive in terms of current operational performance. However, they may be of interest to investors willing to wait 2 to 4 years and bet on a long-term strategic business turnaround.
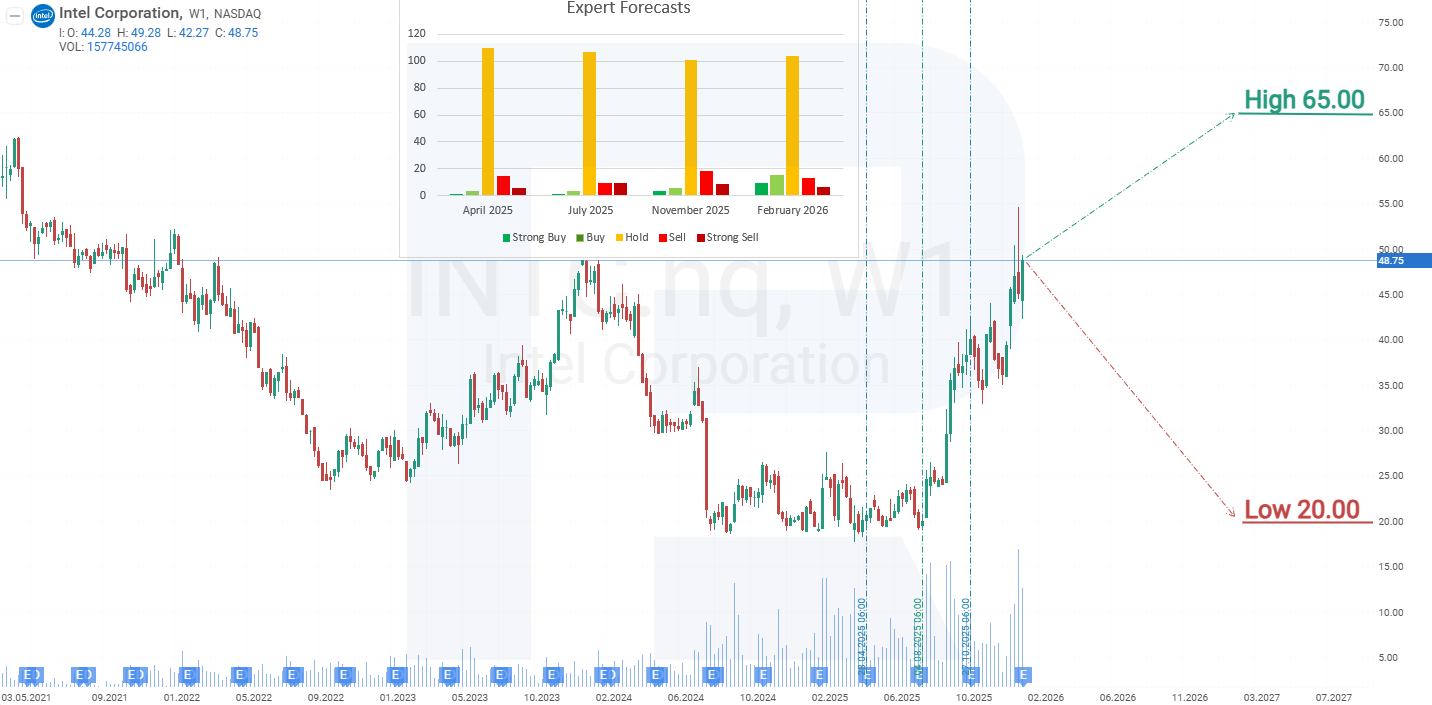
Expert forecasts for Intel Corporation stock for 2026
- Barchart: 5 out of 44 analysts rated Intel Corporation shares as Strong Buy, 1 as Buy, 33 as Hold, 1 as Sell, and 4 as Strong Sell. The upper price target is 65 USD, and the lower bound is 20 USD.
- MarketBeat: 5 out of 37 analysts assigned a Buy rating to the shares, 26 recommended Hold, and 6 rated Sell. The upper price target is 65 USD, and the lower bound is 30 USD.
- TipRanks: 8 out of 32 professionals recommended Buy, 20 Hold, and 4 Sell. The upper price target is 66 USD, and the lower bound is 30 USD.
- Stock Analysis: 4 out of 34 experts rated the shares as Strong Buy, 1 as Buy, 25 as Hold, 2 as Sell, and 2 as Strong Sell. The upper price target is 65 USD, and the lower bound is 20 USD.
Intel Corporation stock price forecast for 2026
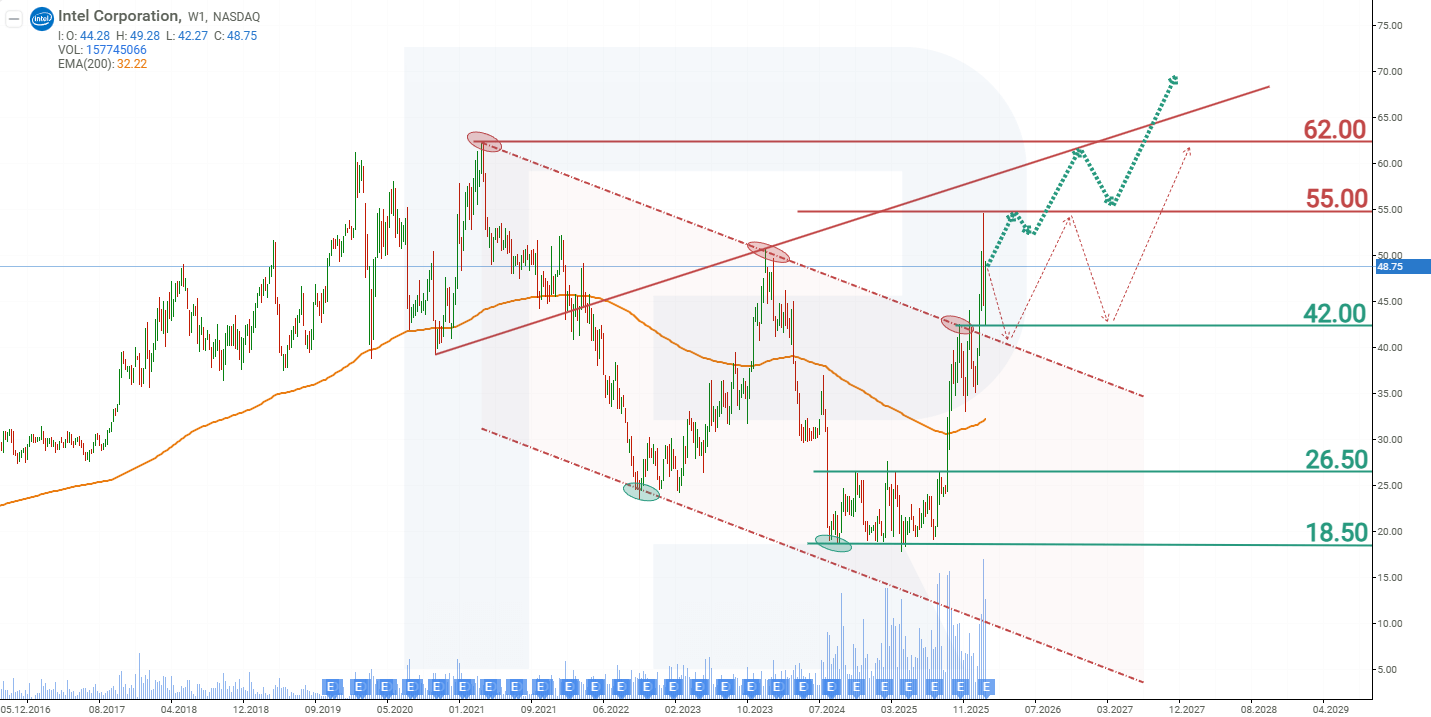
On the weekly chart, Intel shares broke above the descending trendline, signalling the end of the downtrend. Based on the current performance of Intel shares, the potential price scenarios for 2026 are as follows:
The base-case forecast for Intel shares suggests a breakout above the 55 USD resistance level, followed by a rise towards the all-time high of 62 USD. After a brief correction, a breakout above the 62 USD resistance level is expected, with further upside potential for INTC shares.
The alternative forecast for Intel stock suggests a retest of the trendline at 40 USD. A rebound from this level would signal the end of the correction and the resumption of price growth towards the first target at 55 USD. The next target level would be the all-time high at 62 USD.
Intel Corporation stock analysis and forecast for 2026Risks of investing in Intel Corporation stock
When investing in Intel Corporation stock, it is necessary to consider factors that could negatively affect the company’s future revenue. The key factors are outlined below:
- Manufacturing challenges: Intel faces production difficulties, particularly as it transitions to more advanced process technologies. Delays in adopting new practices and overspending on manufacturing projects may lead to higher costs without a corresponding increase in revenue.
- Contract business challenges: Intel’s ambition to become the second-largest contract chipmaker by 2030 faces challenges in attracting clients, intense competition from Samsung and TSMC, and risks associated with this partnership model, which requires significant investments with no guarantee of a return.
- Loss of market share and competition: Intel’s traditional dominance in the PC market is diminishing due to reduced demand. Competition from ARM processors, particularly in mobile devices, servers, and data centres, threatens Intel’s income.
- AI and data centre market: Intel is notably lagging in the AI chip industry, where NVIDIA and AMD hold a significant competitive edge. This has resulted in a loss of market share, particularly in the data centre segment, which is crucial for generating high-margin revenue.
- Suspended dividend payouts: the suspension of dividends, paid consistently since 1992, may discourage investors focused on stable income. Such financial restrictions could erode investor confidence and ultimately push the stock lower.
- Geopolitical and economic factors: tensions between the US and China, a key semiconductor market, could negatively impact Intel’s business in this area. Additionally, the company’s global manufacturing presence is subject to serious geopolitical risks for several reasons.
These factors collectively threaten Intel’s future earnings, potentially leading to a decline in revenue and higher unplanned expenses.
Forecasts presented in this section only reflect the author’s private opinion and should not be considered as guidance for trading. RoboForex bears no responsibility for trading results based on trading recommendations described in these analytical reviews.