- Trading
- Copy trading
- Promotions
- Tools
- Partners
- About us
Trading FAQ
- Why was the position closed at the price, which was not on the chart?Page issue
By default, the charts of trading instruments in the trading terminal show the Bid price, but not all positions are closed at this price.
Long positions (Buy) are opened at the Ask price and closed at the Bid price. Short positions (Sell), in their turn, are opened at the Bid price and closed at the Ask price.
As a result, on the chart you can see only the Bid price, at which your long (Buy) positions are closed.
It can be easily changed by enabling the Ask line in chart settings.
- Why was the order closed without my participation?Page issue
Your order could have been closed due to one of the following reasons:
- Margin level on your trading account reached Stop Out value (current Stop Out values for every account type can be found on "Account types" page).
- The asset price reached Stop Loss or Take Profit.
- Trailing Stop of your position worked.
- How do I open a position?Page issue
Positions in trading terminals can be opened in several ways. The most common of them is the following:
- Choose the required instrument in the panel with quotes (or in other panel that displays instruments).
- Right-click the instrument ticker and choose "New order" from the dialog menu.
- Set order parameters (type, volume, Stop Loss and Take Profit levels).
- Choose the order direction (Buy or Sell) and click the corresponding button.
Also, you can open a new position from the terminal’s main menu or using "One-Click Trading".
- Why was the order not executed at the declared price?Page issue
The following types of orders may be executed not at the declared price: Buy Stop, Sell Stop, and Stop Loss.
When these orders are triggered, the system sends the Market order, which is executed at the current price at the time of the order processing. This is the reason why there might be differences between the price specified in the pending order and the execution price.
Other types of pending orders, Buy Limit, Sell Limit, and Take Profit, are executed at the specified or better price, if such price exists on the market when they are executed.
- What is leverage?Page issue
The leverage is a ratio between the trader’s own funds and borrowed funds, which a trader borrows from his broker. 1:100 leverage means that for a transaction you must have a trading account with amount 100 times less than the sum of the transaction.
Example: a trader chooses the 1:500 leverage and has 200 euros on his account. Leverage 1:500 allows him to buy a contract worth 100.000 euros. - What is a lot?Page issue
Lot is a unit of transactions in trades.
- How does the stop order work?Page issue
A Stop order is a trigger, and when it is reached, a corresponding order Market or Limit is generated by the platform.
There are two types of Stop orders:
- Stop Loss, Buy Stop, Sell Stop. When the asset price reaches the level specified in these order types, the system generates a Market order to buy or sell (Buy Stop, Sell Stop) or close the order to limit losses (Stop Loss).
- Stop-Limit. An order that combines features of Stop and Limit orders. When the asset price reaches the level specified in this order type, the system generates a Limit order at the price set by a trader when opening it.
- How is the profit on financial markets calculated?Page issue
When trading on the financial market, you sell or buy financial instruments expecting their prices to fall or rise in the future.
If, according to calculations, the price is going to rise, a trader opens a buy order. Otherwise, they open a sell order.
The profit is the difference between the price, at which a trader buys or sells the chosen asset, and the price, at which the order is closed (minus spread and (or) the broker’s commission).
Let’s consider a simple example:
You purchased 1 lot EURUSD at 1.2291, which means that you bought 100,000 EUR (1 lot is 100,000 units of the base currency, which is the first symbol in the instrument ticker) for 122,910 (1.2291 * 100,000).
After a while, the price went up to 1.2391 and you closed the position. At that moment, the amount you bought remained the same (100,000 EUR), but due to the price change, it cost 123,910 USD (1.2391 * 100,000).
Your profit will be 123,910-122,910 = 1,000 USD.
- How is a Swap calculated?Page issue
On the financial markets, clients are charged with Rollover (Swap) charges for transiting the position over midnight. The amount of Swap depends on the difference between bank rates of the base currency and secondary currency in a currency pair. Swaps can have either positive or negative value.
RoboForex swap rates are established in accordance with swap rates from our liquidity providers. Current swap rates for each trading instrument can be found in "Contract Specifications" section of our website.
- Why can I not sell at the weekend?Page issue
At weekends, the Forex market is closed, just like other global stock exchanges.
- How risky are operations on the financial markets?Page issue
Trading currencies, stocks, and other investment products is of the market nature and always involves significant risks. Because of sharp market fluctuations, you may both make much of your investments and completely lose them.
You may manage the risks (the ratio of possible financial losses to profits) by using the leverage value, and specific types of orders (Stop Loss / Take Profit) or other available tools. You should always remember that the higher the leverage and possible profit, the higher the risk level.
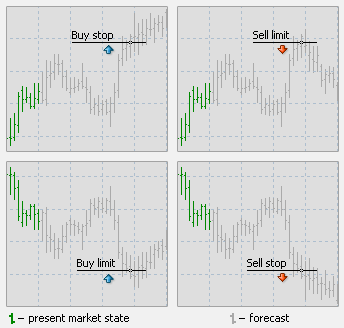
- What types of pending orders are there?Page issue
A pending order is the client's order to buy or sell a financial instrument at the specified price in the future.
There are four types of pending orders:
Buy Limit — to buy, when the future "Ask" price is equal to the specified value. The current price level is higher than the value of the placed order. Execution of this type of order means that the transaction will be made at the price specified in the order or at the price that is lower. Orders of this type are usually placed in anticipation that the instrument price, having fallen to a certain level, will increase.
Buy Stop — to buy, when the future "Ask" price is equal to the specified value. The current price level is lower than the value of the placed order. Execution of this type of order means that the transaction will be made at the price existing at the moment when the order is executed, which may be different from the price specified in the order. Orders of this type are usually placed in anticipation that the instrument price, having reached a certain level, will keep increasing.
Sell Limit — to sell, when the future "Bid" price is equal to the specified value. The current price level is lower than the value of the placed order. Execution of this type of order means that the transaction will be made at the price specified in the order or at the price that is higher. Orders of this type are usually placed in anticipation that the instrument price, having rising to a certain level, will decrease.
Sell Stop — to sell, when the future "Bid" price is equal to the specified value. The current price level is higher than the value of the placed order. Execution of this type of order means that the transaction will be made at the price existing at the moment when the order is executed, which may be different from the price specified in the order. Orders of this type are usually placed in anticipation that the instrument price, having reached a certain level, will keep decreasing.
Ask
Our consultant will answer your question shortly.
